|
GALAPAGOS ISLANDS - 6th Waypoint
Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site, or visit HOME
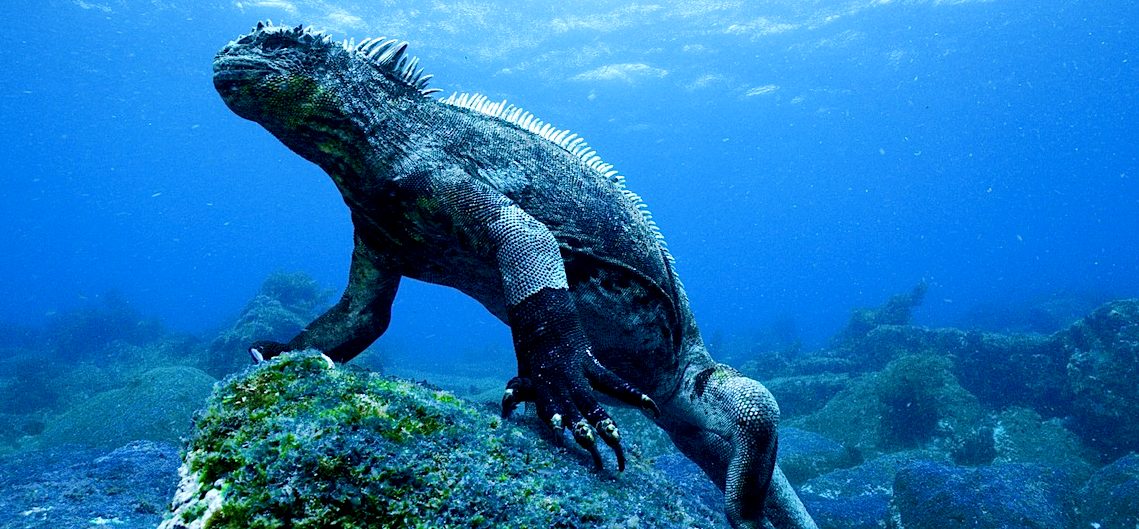
The Galapagos Islands, part of the Republic of Ecuador, are an archipelago of volcanic islands distributed on either side of the equator in the Pacific Ocean surrounding the centre of the Western Hemisphere, 906 km (563 mi) west of continental Ecuador. The islands are known for their large number of endemic species and were studied by Charles Darwin during the second voyage of HMS Beagle. His observations and collections contributed to the inception of Darwin's theory of evolution by means of natural selection.
When specimens of birds were analyzed on his return to
England, it was found that many apparently different kinds of birds were species of finches, which were unique to islands. These facts were crucial in Darwin's development of his theory of natural selection explaining evolution, which was presented in On the Origin of Species.
In late June 2018, Sierra
Negra, one of five volcanoes on Isabela and one of the most active in the Galapagos archipelago, began erupting for the first time since 2005. Lava flows made their way to the coastline, prompting the evacuation of about fifty nearby residents and restricting tourist access.
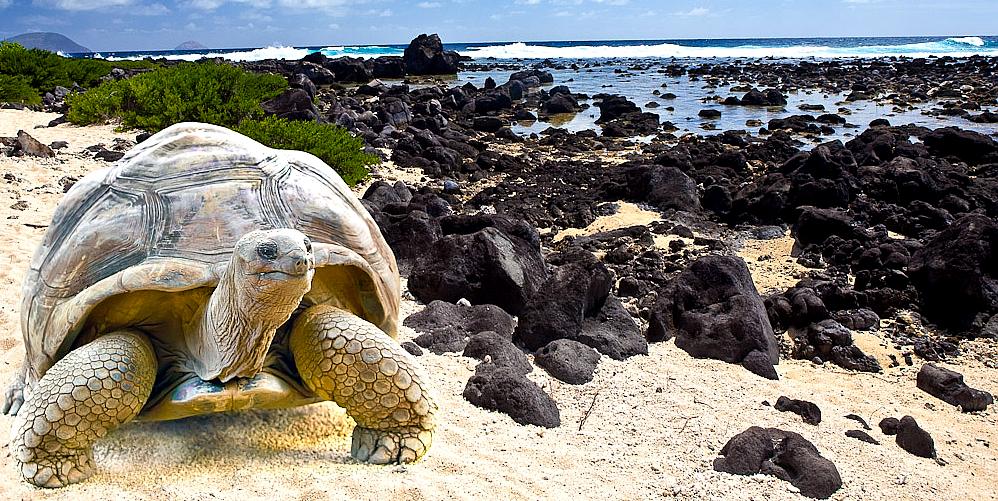
The Galápagos Islands first appeared on the maps of Gerardus Mercator and Abraham Ortelius, in about 1570. The islands were named "Insulae de los Galopegos" (Islands of the Tortoises) in reference to the giant tortoises found there. Until the early 19th century, the archipelago was often used as a hideout by mostly English pirates who attacked Spanish galleons carrying gold and silver from South America to Spain.
In 1793, James Colnett described the flora and fauna of Galápagos, and suggested the islands could be used as base for the whalers operating in the Pacific Ocean. He drew the first accurate navigation charts of the islands. Whalers and maritime fur traders killed and captured thousands of the Galápagos tortoises to extract their fat. The tortoises could be kept on board ship as a means of providing of fresh protein, as these animals could survive for several months on board without any food or water. The hunting of the tortoises was responsible for greatly diminishing, and in some cases eliminating, certain species. Along with whalers came the
fur-seal hunters, who brought the population of this animal close to extinction.
6TH LEG - The sixth leg of this zero carbon voyage is approximately 3640 nautical miles. At a cruising speed of 7 knots this leg from Puerto Ayora (Galapagos) to Tahiiti would take 22 days to complete. At 6 knots the journey would take 25.5 days.
OCEAN AWARENESS - PROVISIONING & MEDIA STOPS
We are making allowance for nineteen (19) provisioning and Public Relations stops of three days duration each. This adds an extra 57 days to the expedition in the interests of furthering awareness objectives. Hence, the passage would not be an outright race, unless any consortium providing financial incentives decided not to stop for photo opportunities by way of a condition in accepting support. If a race was decided on, provisions for a 3-4 person crew would need to be stored on board. Being solar and wind powered there is no need for conventional refueling.
RECORD HOLDER - On the 4th of May 2012, history was made, as Raphael Domjan, at the helm of a giant of a catamaran powered only by solar panels crossed the finishing line at Monaco to become the first electric boat to sail around the world. MS Tûranor PlanetSolar, known under the project name PlanetSolar, was (@ 2018) the largest solar-powered boat in the world. The vessel was launched on the 31st March 2010, also going into the Guinness Book of World Records with a time of 584 days to better by any contender. The project was mostly financed by Immo Stroeher, the owner of the boat. Though a magnificent endeavour, PlanetSolar was not designed at the outset to take full advantage of energy from nature, but was rather a very much modified ferry design.
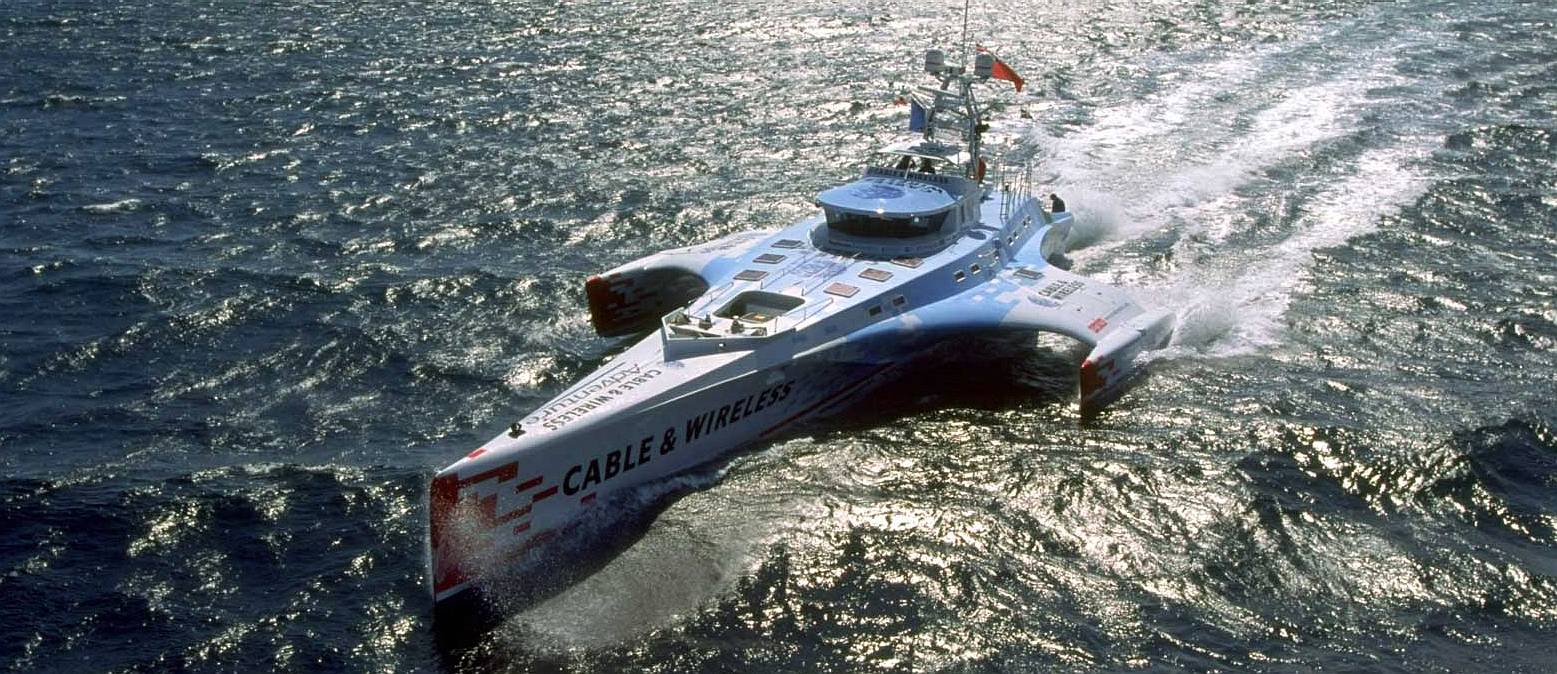
FOSSIL FUELS - The Cable and Wireless Adventurer was built for the purpose of circumnavigating the world in less than 80 days. This was successfully accomplished in July 1998 in 74 days, 20 hours, 58 minutes, traveling more than 22,600 nautical miles (26,000 miles or 41,855 km). This achievement set a new Guinness World Record for a diesel powered vessel. The nautical mile or knot, is a unit of speed equal to approximately 1.15078 miles per hour on land (1.852 km). Solar power cannot compete with diesel engines. This boat is though one of the links in the evolution, or archaeology of efficient hulls.
CLIMATE CHANGER - The above table illustrates one of the most likely ocean awareness expedition routes, known as the 'Sunshine Route,' showing the time elapsed in days for 7 knots average cruising speed, including times for 5 and 6 knot averages - allowing for 10% downtime and 36 days in ports. Hence, although the objective is to reduce the current solar circumnavigation record from 584 days, the event in not an outright non-stop yacht competition in the offshore racing sense. It remains to be seen how accurate such a prediction might be. In this table we only allowed 36 days for provisioning and PR but added a 10% contingency for servicing, that could be used for additional time in ports. As a Climate Changing event, performance is one of the main criteria, especially concerning the possibilities for a transition to low carbon shipping and the contribution this might make in combating global warming.
LINKS & REFERENCE
https://www.planetsolar.org/ http://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/first-circumnavigation-by-solar-powered-boat
This website is provided on a free basis as a public information service. Copyright © Cleaner Oceans Foundation Ltd (COFL) (Company No: 4674774) 2024. Solar Studios, BN271RF, United Kingdom. COFL is a charity without share capital.
|